Today’s article is about Marketing Abstract.
Marketing Abstract
Background
Customers are the king for any business whether it is manufacturing or service oriented in nature. In modern competitive age, organization design their services focusing the different form of customers i.e. prospective, current and lost customers. Evaluation of Service Encounter Satisfaction is essential to develop long run competitive position over the rivals in competitive market.
Study Objectives
The main objective of this study is to measure how different service encounter contributes on customer satisfaction based on some super shop of Dhaka city.
Methodology
This study is a quantitative in nature where both primary and secondary data has been used. The customers who purchase frequently from super shop are considered as population. Primary data has been collected from a total of 110 samples.
The purposive method of sampling has been used to determine the sample size. Primary data has been collected through a structured questionnaire which has been prepared as per Likert scale 5 point methods. The questionnaire has been designed basing on three specific hypotheses. SPSS version-23 has been used to analyze the primary data. Descriptive statistical tools e.g. mean, standard deviation, standard error mean etc. has been used. T-test has been used to test the hypotheses.
Findings
The study reveals that, the customers of super stores are not satisfied regarding the initiative taken by authority on post service encounter. Based on the findings, some recommendations are given in order to ensure customer satisfaction on post service encounter. The paper will be helpful to the authorities of super shops to develop their strategies in order to design services focusing customer’s needs at different stages.
1. Introduction
Now a day’s super shop is a popular concept in Bangladesh, especially in city and divisional areas. Super shops introduced a whole new window in the shopping of daily necessities. These shops offer quality products at a stable price in safe and clean environment. It is now a growing version of retail business in city area.
There are number of reasons of the popularity of this form of business. Among them busiest life style, increase of the duel career couple, high living cost, excessive traffic jam, quality of the service, increase of income and consciousness of the customers, quality products, products variety and special products, locations, hygienic environment, hassle free shopping, competitive price, service and layout of the shops etc. are mainly influencing factors for expanding this form of business.
Basically, the customers of super shops are comparatively higher income group people of the society. So, they want quality products and services rather than traditional shopping places. Along with the quality products, the customers also want to minimize their time and hazards for shopping.
History of Super shops
The first Real Canadian Super shop location opened in March 1979 in a former Loblaws location in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan under the name SuperValu. Numerous other SuperValu locations opened across Western Canada before most gradually expanded into Superstore sites.
The SuperValu name is still in use in British Columbia and the Maritimes, the latter branded as Atlantic SuperValu. The similarly named The Real Superstore was used in the United States from the 1970s up until the mid-1990s by the Loblaws-owned National Supermarkets chain until the chain was purchased by competitor Schnucks.
Supermarket diffusion in developing countries has occurred in three waves, so far, starting in the 1990s with much of South America, East Asia (outside China) and South Africa. This was followed by a second wave in the mid-to-late 1990s, including Mexico, Central America and much of Southeast Asia. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, a third wave hit China, India and Vietnam.
Departmental Stores
A departmental store is a retail trade shop which is a strategic place to satisfy customers by giving him or her the choice of selecting all that he or she wants. There are number of departmental stores in Dhaka like Agora Departmental Store, Aqib Departmental Store, Trust Family Needs shop etc.
Supermarkets
In the modern era, a popular place for the shopping is supermarkets that are a self-service environment. All the supermarkets want to build a good relationship with their costumers and they are looking for more costumers. They want to track the customer satisfaction in the supermarket surroundings,
Super Shops in Bangladesh
The history of retail super shop of Bangladesh is not too old. It has started in the year 2001. Agora is the first retail store in Bangladesh who operates as a chain of hypermarkets, discount department stores and grocery stores. After the breakthrough made by the pioneering Rahimafrooz Group more than 120 super shops outlets have been set up in Bangladesh by around 40 companies over last 16 years.
The industry is mainly dominated by three major players. These are Shwapno who has 59 outlets, Agora with 13 outlets and Meena Bazar with 18 outlets. With rapid urbanization, the industry is expected to grow by almost 15 times than its current size by 2021.
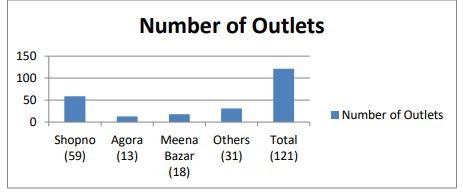
The main obstacle in the expansion of super shop is the supply chain. The distribution system is still not well organized. As a result, the goods are not delivered to the shops on time. Moreover, still it is time consuming to get the necessary permissions to open the super shop, sometimes even a year or more. It also requires dealing with distributors and suppliers, some of whom are unprofessional. On the other hand, Bachmann (2008) shows in his writings that a majority of Bangladeshi customers will not change their shopping habits anytime soon.
The costs of opening up a single superstore in Bangladesh are at least four times as much as those of neighboring countries. The Bangladesh Super Shop Owners Association (BSOA) identified three major challenges for the superstore business in Bangladesh. The challenges include opening up a new mall and its forced shut down, uneven VAT scenario in the market and harassment in the name of food safety
Organized retail is booming and creating huge opportunities for enterprises. Retailers though sell other companies’ products work out their own marketing strategies fixing their own target market towards providing customer satisfaction separately. Retail stores irrespective of product line and relative prices emerge in all shape and sizes, such as Specialty stores, Department stores, Supermarkets, Superstore, Convenience stores, Discount stores and Off-price stores!?].
Service Encounter
A service encounter is a period of time during which customer interact directly with a service. It is also called as “Moment of Truth”. A moment of truth is usually defined as an instance where the customer and the organization come into contact with one another in a manner that gives the customer an opportunity to either form or change an impression about the firm.
Many services especially those classified as high contact involve numerous encounters between customers and service employees, either in person or remotely by phone or e-mail. Service encounters may also take place between customers and physical facilities or equipment. In low- contact services, customers are having more and more encounters with automated machines that are designed to replace human personnel.
Customer interaction may provide two types of outcome like Moments of Magic and Moment of Misery. Favorable moments of truth have been termed as ‘moments of magic’. These are instances where the customer has been served in a manner that exceeds his expectations through better services. On the other hand Moment of Misery represents the situation where the customer interaction has a negative outcome due to poor customer services.
A positive service encounter is definitely essential in competitive market to attract and retained the customer with the business. It provides distinctive positions over the rivals in a competitive market. So, every business should focus on its service encounter. Moreover, in today’s increasingly service driven markets and with the proliferation of multiple providers for every type of product or service, moments of truth have become an important fact of customer interaction that marketers need to keep in mind while designing services.
Customer Experience
Customer service experience is the sentiment associated with a company’s ability to provide positive experiences to their customers. Services range from one-on-one interactions where a support agent resolves a customer issue, to exchanges with the brand on a more public scale. In commerce, customer experience is the product of an interaction between an organization and a customer over the duration of their relationship. This interaction is made up of three parts i.e.
i. The customer journey;
ii. The brand touch points through which the customer interacts;
iii. The environments that the customer experiences (including digital environment) during their experience.
A good customer experience means that the individual’s experience during all points of contact matches the individual’s expectations .
Service encounter is any discrete interaction between the customer and the service provider relevant to a core service offering including the interaction involving provision of the core service offering itself. This interaction can occur into 3 stages of getting services. These stages are showing bellow with table;

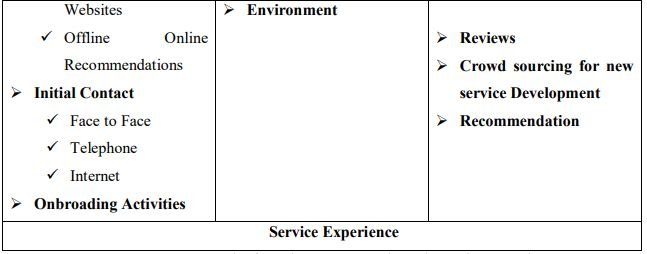
Pre-core service encounter period as the time interval preceding the core service encounters that focuses on leading customers to engage with the firm in the core-service encounter. This period may encompass multiple service encounters[9]. The post-core service encounter period is defined as the time interval following the core service encounter during which consumers assesses and act on their experience in the two previous periods. Through this period, the firm’s goal is to retain customers and to improve future service experiences.
Service Encounter in Super Shop Services in Bangladesh
Like any other service industry, it is vital to measure the service encounter in super shops services. Though today’s marketers are more conscious about customer needs, wants and demands than that of past but still the service provides by the marketer are less smart than any other neighboring countries. Different types of digital devices are available in Bangladeshi market which are using to connect the lost, current and prospective customers.
People of the country, especially in the city areas are becoming more engaged with the super shops due to different reasons like quality products, less time consuming, better customer service, availability of different types of products under an umbrella etc. Today’s customers are also smarter than the past.
They are now become a strategic partner of the service provider. As a result, they always focus on the changes made by the organizations. They always become connected with the service provider so that the service provider can explore the expectations of the customers. Companies are also investing more in maintaining and evaluating the relationship with the customers at different stages of services. The both parties interactions make the service industries smarter than that of past.
2. Literature Review
Service encounter
Service encounter is the face-to-face interactive relation between service provider and service recipient during the process of service consumption. It is also considered as the core of service marketing having considerable impact on service quality control, service delivery systems and customer satisfaction etc.. Service encounter is a period of time during which a consumer directly interacts with a service.
Service encounter is the dyadic interaction between a customer and service provider. Moreover, the service encounter perspectives mentioned here as an important criteria or attributes against which customers assess or evaluate service providers. The concept of these service encounter attributes is highly similar to some perspectives of service quality .
Physical environment is usually one of the significant factor affecting consumers’ ultimate satisfaction with a service. The physical environment may help or hinder the achievement of internal organizational objectives and external marketing objectives.
For consumers, evaluation of a service firm often depends on evaluation of the service encounter or the period of time when the customer interacts directly with the firm. Researchers need to consider simultaneously all periods of the service experience like pre-core service encounter, core service encounter and post-core service encounter to make valuable contributions to the literature
Services Marketing Mix
The marketing mix is defined as the controllable variables that an organization can coordinate to satisfy its target market . Because of the distinguishing characteristics of services, it has been suggested that service firms have additional variables, beyond the traditional “four P’s” that can satisfy target markets .
Booms et. al., proposed an expanded marketing mix for services consisting of the four traditional elements like product, price, place, promotion and three new ones such as physical evidence (the physical surroundings and all tangible cues), participants (all human actors in the service encounter including firm personnel and other customers) and process (procedures, mechanisms, and flow of activities) .
There are three key players in marketing exchange relationships. These are the company, the customer and the employee. The three players can be depicted as vertices in a triangular framework (currently referred to the literature as the “triangle model of services marketing” with three possible dyadic links
Customer Satisfaction
Since the 1970s researchers have focused on understanding consumer satisfaction. Customer satisfaction is widely recognized as a key pressure in the information of customers future purchase intentions.
Satisfied customers are also likely to tell others favorable experience and thus engage in positive work of mouth advertising. Organized retailers need to enhance customer satisfaction in terms of ensuring product quality, store convenience, after sales services, availability of new products and lure buyers with attractive promotional schemes Gaining high level of customer satisfaction is very significant to any business.
A satisfied customer is most likely to be loyal and to make repeat orders and to use a wide range of services offered by a business. Customer satisfaction is an asset that should be monitored and managed just like any physical asset. Two key elements of service satisfaction for customers are the perception that they have at least some control or choice and that the service provider is being fair .
Customer Retention
Customer retention has received considerable attention. It has become a prime issue for food retail organizations desiring to stay in business, increase footfall, maximize profits or build and sustain the competitive advantage in the food sector. CRM can play a vital role for retaining the customers. The top management need to be conscious about maintain the relationships which will help to retain the customers.
The above literature review shows that number of research works available on customer satisfaction focusing on different sectors. But a few work has done on service encounter satisfaction focusing the three specific stages. This research has emphasized on customer satisfaction evaluation when they interact at different stages and tried to find out their response in each stage.
3. Research Problem
Number of researches have been conducted on customer satisfaction on product or services of different industries by different scholars from both home and abroad. But a few researches are available about service encounter. Moreover, the research on service encounter of superstores is absolutely absent in Bangladesh. We have seen a customer can get benefit from three specific stages of service like pre, during and post shopping stage. Most of the organization focuses on during stages to satisfy customers.
The satisfaction at the other stages is much important than during stages for attracting and retaining the customers. This study has been conducted focusing the three stages to know about the satisfaction on the said three stages focusing on super shop.
Customers may be three types like lost, current and prospective. If company can concentrate on the satisfaction on service encounter it may attract the lost and prospective customers. Though, the super shop is the growing sector for daily shopping, so it is the time to work on service encounter of the industry.
4. Objectives of the Study
The main objective of the study is to measure how different service encounter contributes on customer satisfaction. Along with main objectives, the study will also meet the following supportive objectives;
i. To identify the encounters which will mostly contribute on customer satisfaction;
ii. To identify the limitations in service encounter to satisfy the customers;
5. Hypotheses of the Study
The study has been conducted basing on the following hypothesis;
H₁: The customers of super shop are satisfied on pre-core service encounter stage.
H2: The customers of super shop are satisfied on during shopping stage.
H3: The customers of super shop are satisfied on post-service encounter stage.
6. Methodology of the Study
This study is mainly quantitative in nature to measure the customer service encounter satisfaction basing on primary data from the customers who deliberately shop from different super shops.
6.2 Study Area
The area of the study is Dhaka city. Primary data has been collected from the customers directly through pre-defined close ended questionnaire. Here customers mean who shops frequently from different super shops of Dhaka city.
6.3 Population, Sample design and size
In this study, the customers who purchase from the super shop are considered as population. Different service provider of super shop also considered as the institutional population. The sample respondent of the study is 110. These sample size has been taken by applying purposive method and the questionnaire has been distribute randomly among the samples.
6.4 Data Collection Methods
In this study, both Primary and secondary data has been used. Primary data has been collected from the respondents through questionnaire. Secondary data has been collected through studying different articles, journals, newspapers, websites, books etc.
6.5 Questionnaire
A structured questionnaire has been developed to conduct the study. The questionnaire has developed as per Rensis Likert 5 point basis. The 5 points are strongly satisfied, satisfied, neutral, dissatisfied and strongly dissatisfied. These 5 points are converted with numerical values respectively 5,4,3,2 and 1 for the analysis.
6.6 Analysis of the Collected Data
The collected data has been analyzed with Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version-23. Descriptive statistics including mean, standard deviation, standard error mean and one tail t-test have been done to analyze the perception of respondents. Here, the test level is considered as 3 and the confidence level is considered as 95% level of significance.
7. Limitations of the Study
The study has been conducted basing on the super shop operating in Dhaka city. Number of super shop is available in the city in order to meet the consistent demand of customers. The primary data has collected from the users of these shops from different super shop. The research work will be more accurate if the study is basing on a specific institution’s customers. On the other hand, the size of the sample is too small.
Though the population size is unknown, the sample size should be 385 as per Cochran Formula of Sample Size calculation. So the small size of sample is one of the limitations of the study. On the other hand, the sample respondents have collected from the users of Dhaka city only.
The research may provide more appropriate results having data from other cities. However, along with the above limitations, the research will be a good guideline provider for the future researchers and also will be effective to the policy maker, super shops, customers and other concerned parties.
8. Analysis and Findings
The analysis of the collected primary data is presenting bellow;
Descriptive Statistics
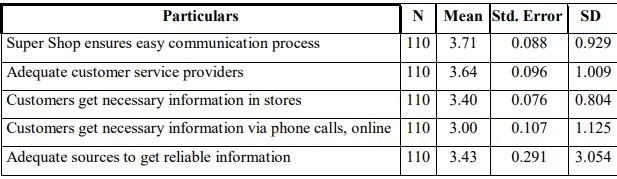
The above table shows that the mean value of customers’ satisfaction on the pre-core service encounter stage. The table shows that the customer response on “super shop ensures easy communication process” is higher (mean=3.71, SD=0.929) among the five variable where the mean value of customers response on “Customers get necessary information via
phone calls, online” is lower (mean=3.00, SD=1.125). The table also shows that, the customers’ response for all variables is greater than average value 3.00 which indicates that customers are satisfied about pre-core service encounter stage.
Descriptive Statistics
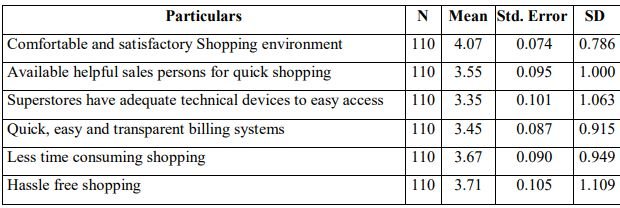
The above table shows that the mean value of customers response on customers satisfaction on the service encounter of core stage. The table shows that the response on “Comfortable and satisfactory shopping environment” is higher (mean=4.07, SD=0.786) among the five variable where the mean value of customers response on “superstores have adequate technical devices to easy access” is lower (mean 3.35, SD 0.101).
The table also shows that, the customers’ response for all variables is higher than average value 3.00 which indicates that customers are satisfied about service encounter at during shopping or core stage.
Descriptive Statistics
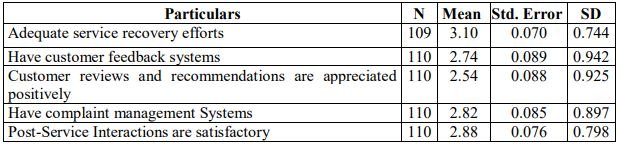
The above table shows that the mean value of customers’ responses on the post service encounter satisfaction. The table shows the perceptions on “adequate service recovery efforts” is greater (mean=3.10, SD=0.741) among the five variable where the mean value of customers perceptions on “customer reviews and recommendations are appreciated positively” is lower (mean=2.54, SD=0.925).
The table also shows that, the customers’ response for all variables is lower than average value 3.00 except “adequate service recovery efforts” which indicates that customers are not satisfied about post service encounter.
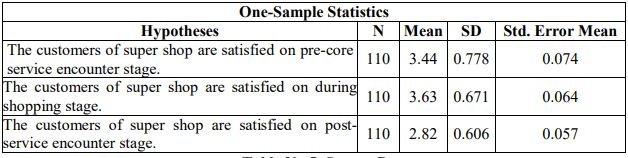
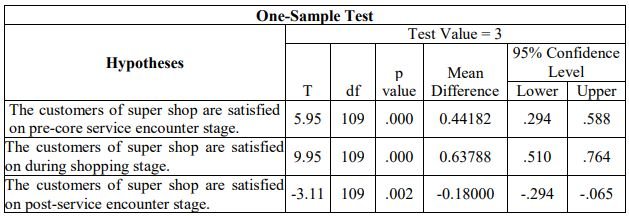
The table-5 shows that, the mean value of Customer satisfaction on “Super shop’s Pre-core Service Encounter is satisfactory to the customers” is 3.44 and the SD is 0.778. On the other hand, table 5 shows that t value is 5.95 and the p value is 0.000. It represents that the hypothesis is accepted that is customers are satisfied about the pre-core service encounter of super shop’s service.
It is also noticeable that, the mean value of customer satisfaction on “Super shop’s service encounter is satisfactory during shopping (core stage) to the customers” is 3.63 and the SD is 0.671. On the other hand, table 5 shows that t value is 9.95 and the p value is 0.000. It represents that the hypothesis is accepted that is customers are satisfied about the service encounter of super shop’s service during shopping or core stage.
On the other hand, the mean value of customer satisfaction on “super shop’s post service encounter is satisfactory to the customers” is 2.82 and the SD is 0.606. On the other hand, table 6 shows that t value is -3.113 and the p value is 0.002. It represents that the hypothesis is rejected. Customers are not satisfied about the post service encounter of super shop’s service.
9. Conclusions and Recommendations
9.1 Conclusions
In modern era every organization invest more to satisfy the customers’ needs. Customer’s needs are diversified because every customer is unique in terms of tastes, choice and habit. Due to the excessive busy life, the demand of super shop is increasing day by day.
Peoples are becoming dependent on super shop for daily household shopping. Especially the scenario is very common in city areas. As a result of this dependency, the tendency of building super shop is also increasing day by day. Customers are getting better service and also quality products with reasonable price from this super shop.
However with the quality products and services, the customers have also some implied needs from the super shop. Like other organization, super shop also requires to satisfy its customers. The service provider requires satisfying the customers at the three stages of services like pre-shopping stage, during shopping stage and post-shopping stage.
This study has found that the customers of super shops are satisfied about the service of pre and during or core shopping stage service but they are not satisfied about the post stage. In the modern competitive business era, super shop authority needs to concentrate on post stage needs of customer in order to hold them as future customers. Otherwise, the on growing dependency of customers towards super shop may not be continued.
9.2 Recommendations
On the basis of the findings, the researchers suggest the following initiatives to the authorities of super shops;
i. Super shops’ authority should focus on creating long run relation with current and future or even lost customers. To build such relations, the authority may focus on post service encounter satisfaction to the customers. The authority should maintain post- service interactions satisfactory to the customers for making them future customers.
ii. Super shops’ authority need to ensure feedback from the current customers about products/services. They also can develop complain management systems (CMS) which will handle the customers complain about the service.
iii. Super shops’ authority can accept the customer reviews and recommendations positively. Modern digital mode i.e. Facebook, mail or even websites etc. can be used for the purpose. Efficient manpower can be appointed to handle the customer reviews and recommendations. The authority can also increase the use of phone calls, websites Facebook etc. to provide customers necessary information.
iv. The authority of superstores need to ensure all types of technical devices at the stores available. This will help customers to protect the risk and hazard of bearing cash.
References
1. Wikipedia History of Super stores. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real_Canadian_Superstore#History on 09 June, 2019.
2. Aghaei, M., Mirzaee, H., Djadidi, M., Hassanpour, E., & Salehi, M., (2012). Measure of Customer Satisfaction in the hyper supermarkets in Malaysia. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 2(1), pp. 01-09. Tribune, 8th on 10 June, 2019.
3. Mahmud, A. H., (2018). Why more and more people are leaning towards superstores? Dhaka https://www.dhakatribune.com/business/2018/03/08/people-leaning-towards superstores March, 2018. Retrieved from
4. LightCastle (2019). Market insight: Supermarket industry in Bangladesh Part -1. Retrieved from https://www.lightcastlebd.com/insights/2015/02/16/market-insight- supermarket-industry-bangladesh on 10 June 2019.
5. Bachmann, B. (2008). Supermarkets on the rise. The Daily Star, Retrieved from https://www.thedailystar.net/news-detail-68728
6. Mala, D. A., (2018). Costs of opening superstores in BD among highest in the region. The Financial Express, Retrieved from https://the financialexpress.com.bd/trade/costs-of- opening-superstores-in-bd-among highest-in-the-region-1532231559
7. Armstrong, G., & Kotler, P., (2006). Marketing: An Introduction (8th ed.). Prentice Hill, New Jersey.
8. Thompson, E. & Kolsky, (2004). How to Approach Customer Experience Management.
9. Bitner, M. J., (1995). Building service relationships: It’s all about promises. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 23(4), pp. 241-251.
10. Dolen, M., Willemijn, V., & Ruyter, K., (2002). Moderated group chat: An empirical assessment of a new e-service encounter. International Journal of Service Industry.
11. Surprenant, & Michael R. S., (1987). Predictability and Personalization in the Service Encounter. Journal of Marketing, 51(1), pp. 73-80.
12. Roth, D., Lauber, B. G., Crane, R. D., & Clark, J. A., (1997). Administrative update: Impact of state mental health reform on patterns of service delivery. Community Mental Health Journal, 33(6), pp. 473-486.
13. Winsted, F. K., (1993). Service encounters dimensions: Across-cultural analysis. Published Doctoral Dissertation, University of Colorado at Boulder.
14. Voorhees, C. M., Fombelle, P. W., Gregoire, Y., Bone, S., & Gustafsson, A., (2017). Service encounters, experiences and the customer journey: Defining the field and a call to expand our lens. Journal of Business Research, pp. 1-12.
15. McCarthy, E., (1987). Basic Marketing (9th ed.). Jerome and William D. Perreault, Jr., IL: Richard D. Irwin, Inc. pp. 35.
16. Gronroos & Christian (1984). A Service Quality Model and Its Marketing Implications. European Journal of Marketing, 18(4), pp. 36-44.
17. Booms, B. H., & Bitner, M. J., (1981). Marketing Strategies and Organization Structures for Service Firms. Marketing of Services, James H. Donnelly and William R. George, eds.
Chicago: American Marketing Association, pp. 47-52.
18. Kotler, P., (1994). Marketing Management. Englewood Cliffs. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Inc.
19. Karmugil, S., & Kannapa, R., (2015). A Study on customer satisfaction towards retail stores in Tiruchirappalli Town. International Journal of Advanced Research in Management and Social Sciences, 4(6), pp. 69-78.
20. Malik, M., (2012). A study on Customer’s satisfaction towards service quality of Organized retail stores in Haryana. Indian Journal of Marketing, 42(2), pp. 51-60.
21. Jeevananda, S., (2011). Study on Customer satisfaction level at Hypermarkets in Indian Retail Industry. Research Journal of Social Science and Management, 1(3).
22. Namasivayam, K., & Hinkin, T. R., (2003). The Customer’s Role in the Service Encounter: The Effects of Control and Fairness. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly, 44(3), PP. 26-36.
23. Mia, M. N., (2018). Customer Relationship Management Practices in Private Medical
